ACLS Cases Respiratory Arrest
Individuals with ineffective breathing patterns are considered to be in respiratory arrest and require immediate attention. There are many causes of respiratory arrest, including but not limited to cardiac arrest and cardiogenic shock. Resuscitate individuals in apparent respiratory arrest using either the BLS or the ACLS Survey.
Respiratory arrest is an emergent condition in which the individual is either not breathing or is breathing ineffectively.
If someone is breathing ineffectively, it can be agonal or gasping respirations, which can often go unrecognized.
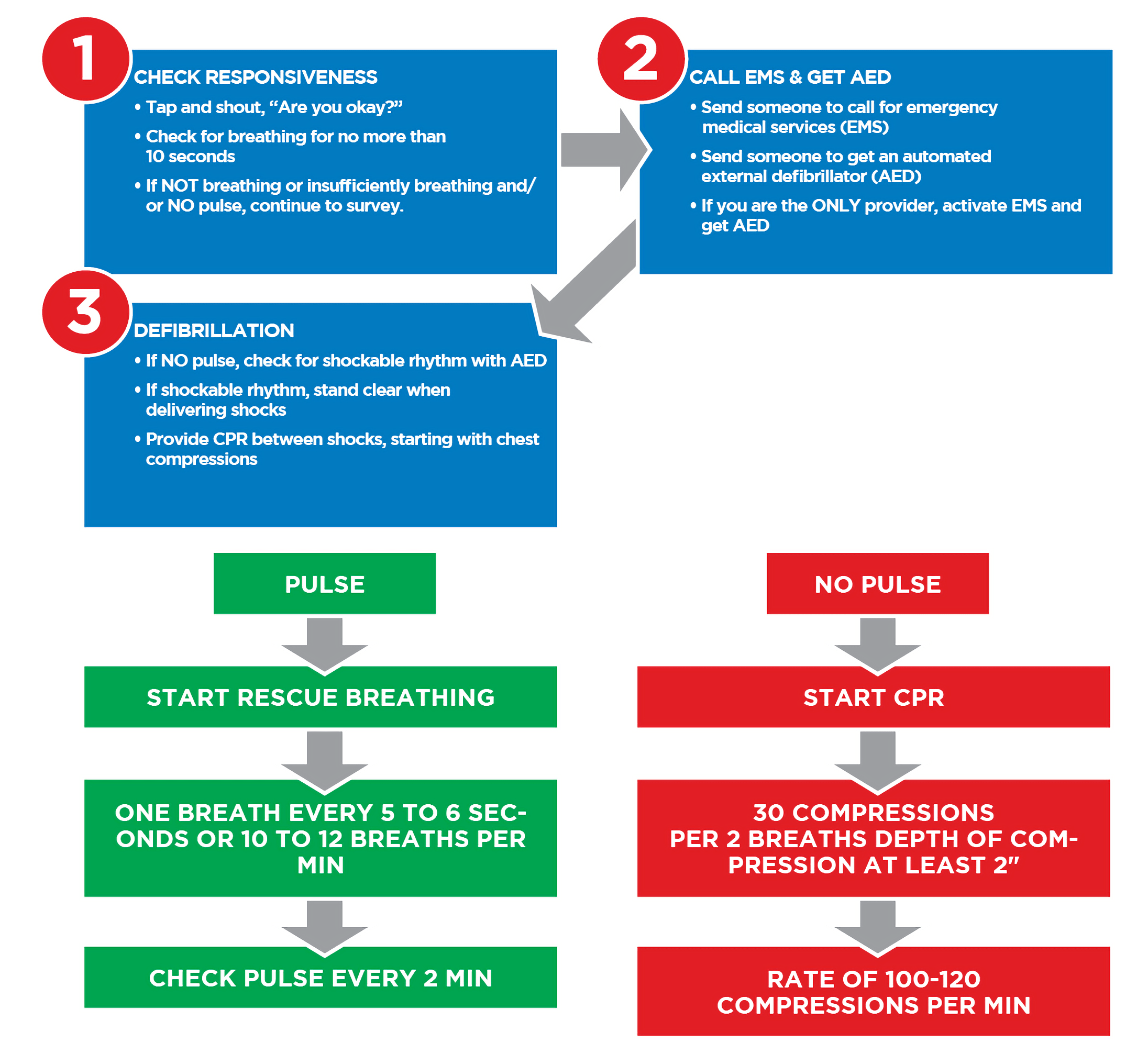
BLS Survey
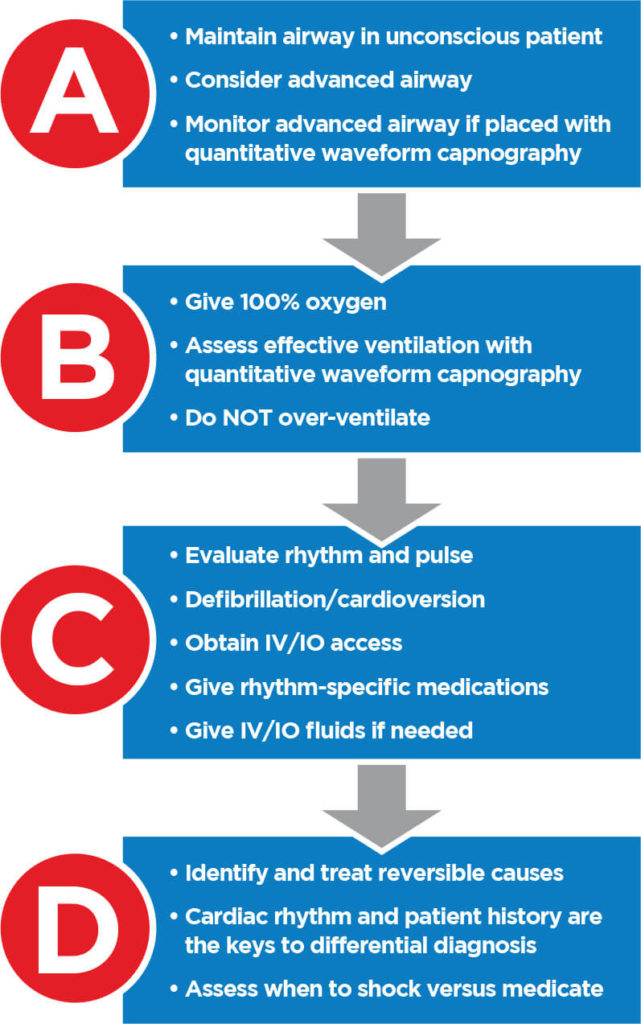
ACLS Survey
TYPE OF AIRWAYS
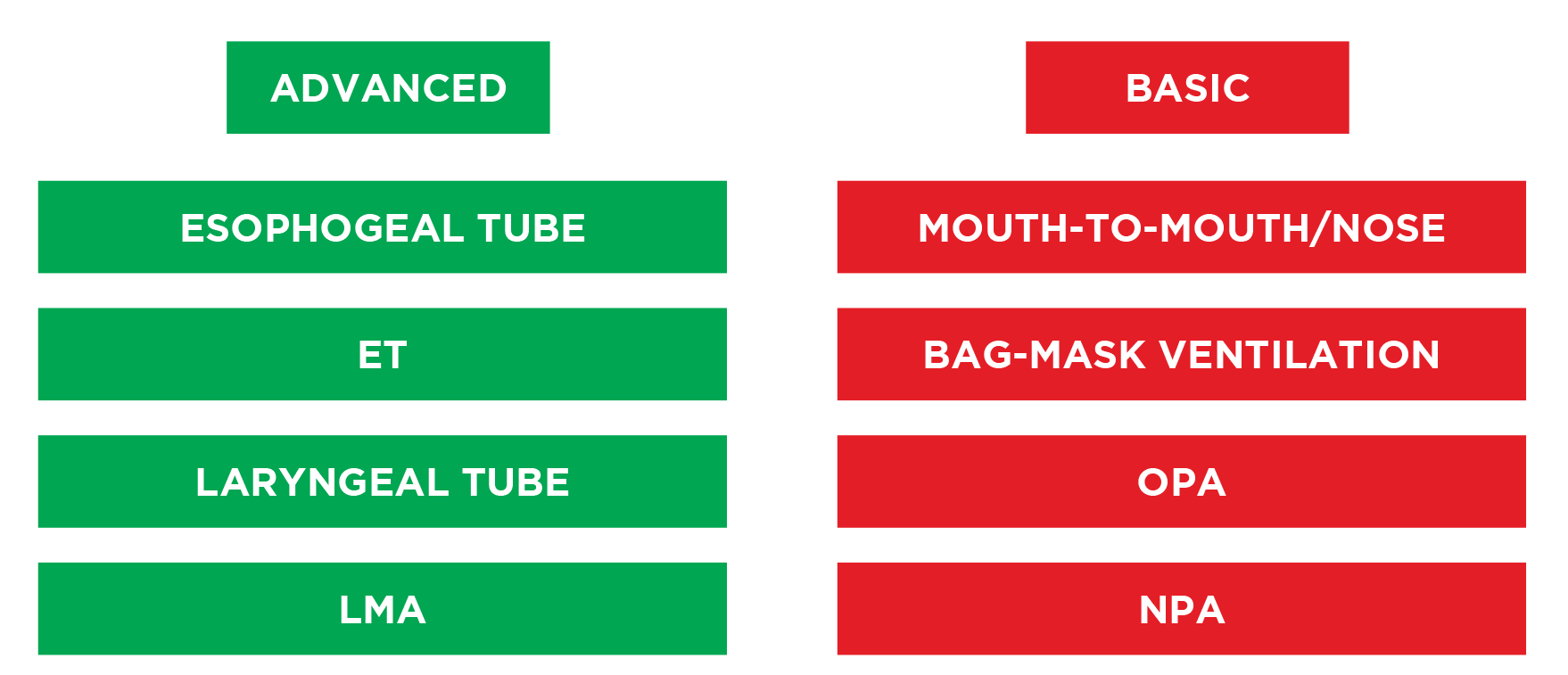
In Table 5, the airways listed in the left column are considered advanced airways, while those in the right column are basic airways. Although OPAs and NPAs
are considered to be basic airways, they require proper placement by an experienced provider. Advanced airway placement requires specialized training which
is beyond the scope of ACLS certification. However, all ACLS providers should be familiar with the proper management of advanced airways in order to be part of
an effective life support team.
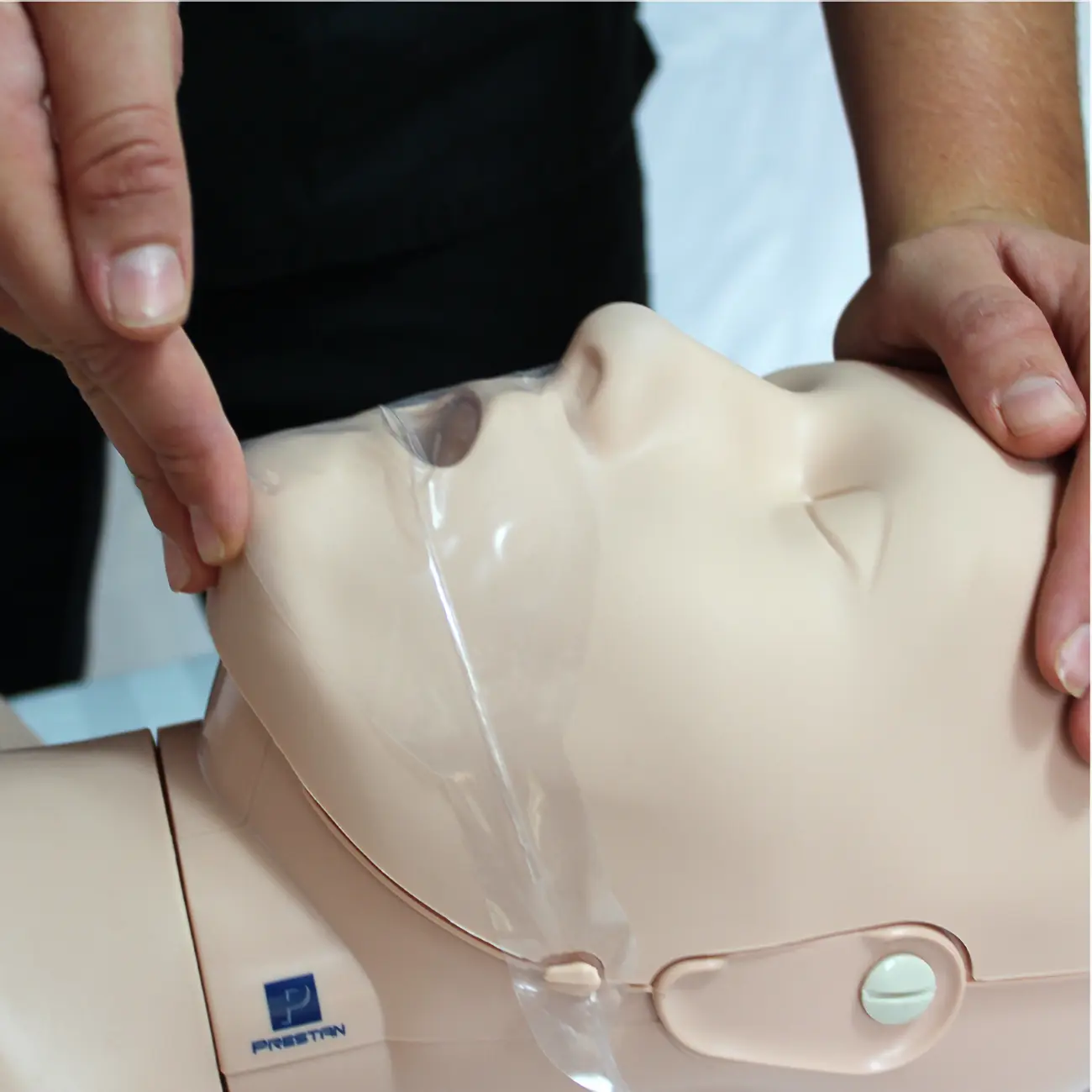
CPR is performed with the individual lying on their back; gravity will cause the jaw, the tongue, and the tissues of the throat to fall back and obstruct the airway. The airway rarely remains open in an unconscious individual without external support.
The first step in any airway intervention is to open the airway. This is accomplished by lifting the chin upward while tilting the forehead back (Figure 22). The goal is to create a straighter path from the nose to the trachea
Do not over ventilate (i.e., give too many breaths per minute or too large volume per breath). Both can increase intrathoracic pressure, decrease venous return to heart, diminish cardiac output, as well as predispose individuals to vomit and aspiration of gastrointestinal contents.





